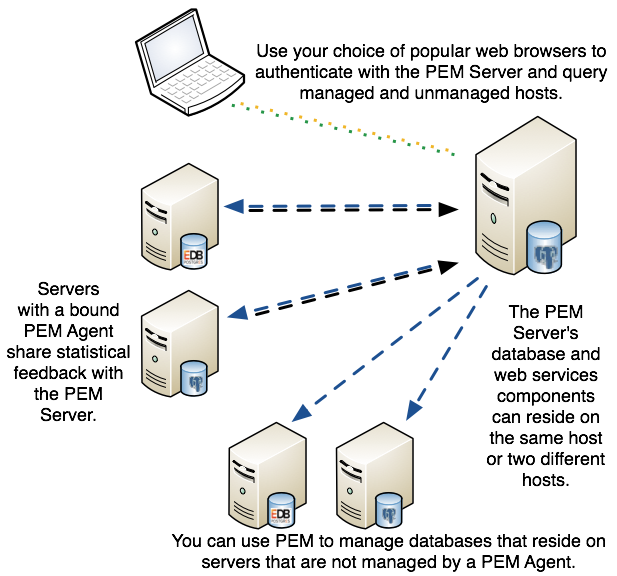
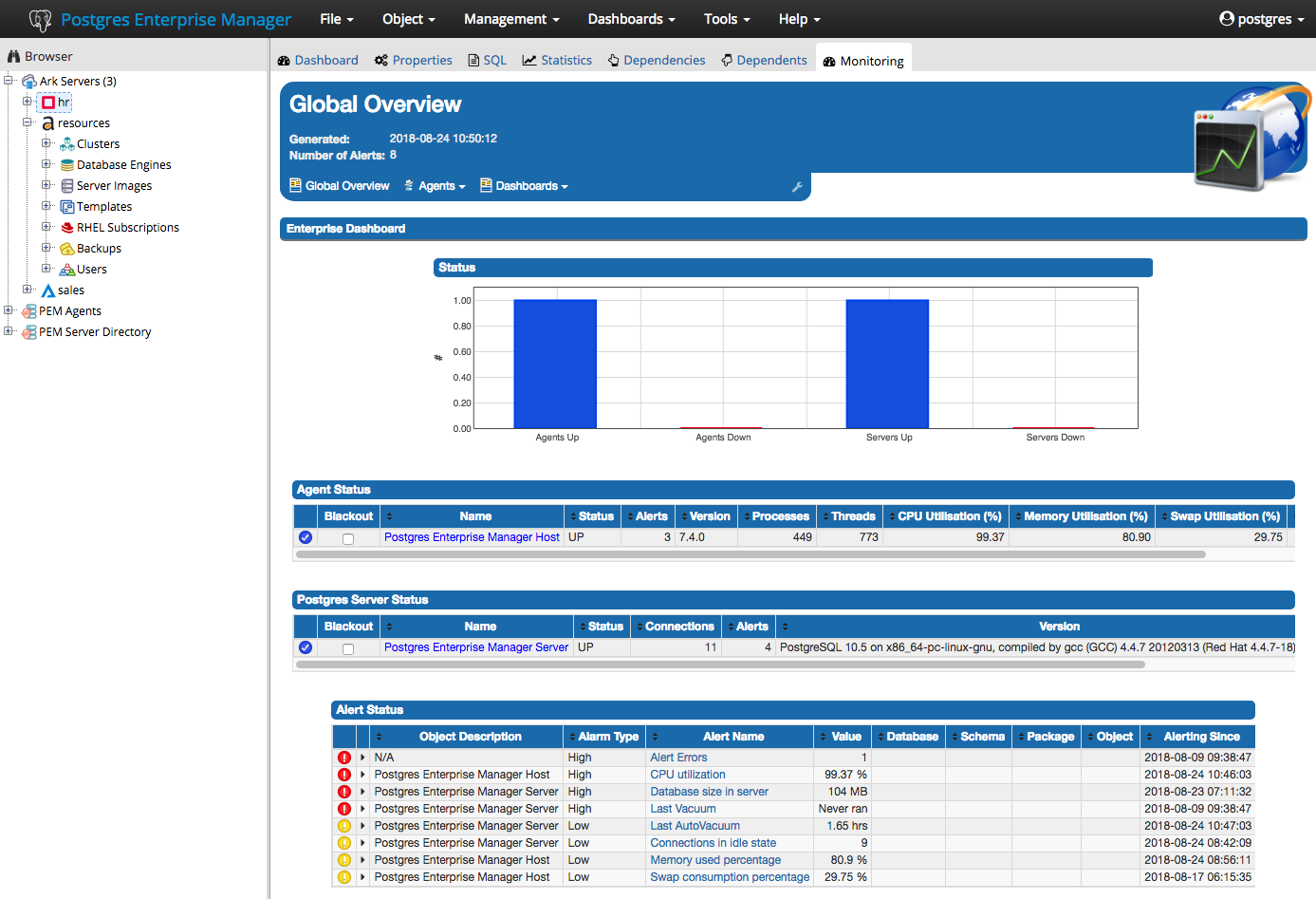
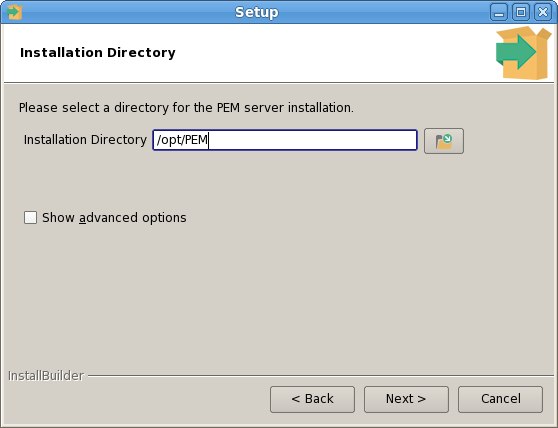
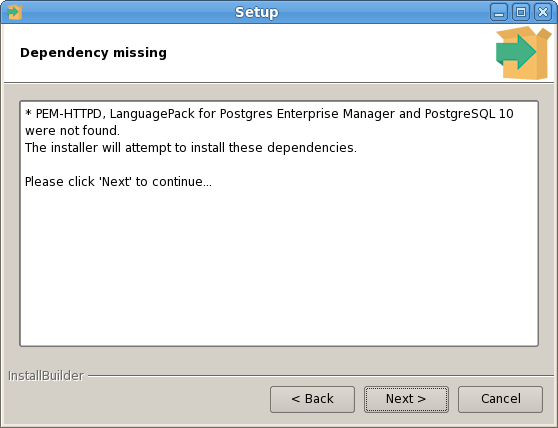
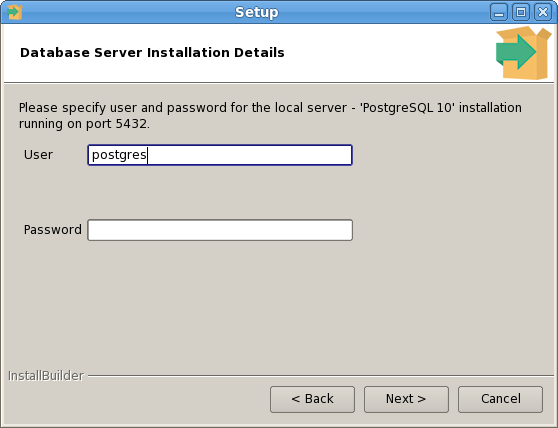
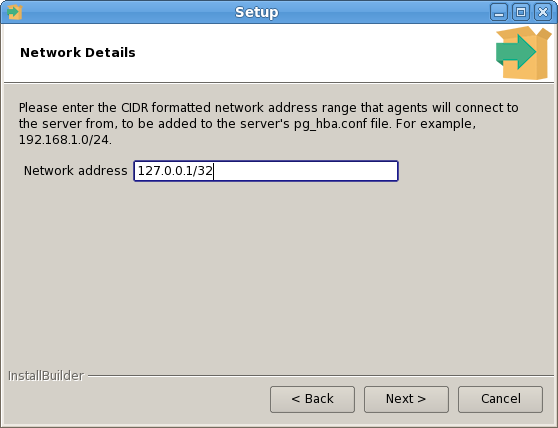
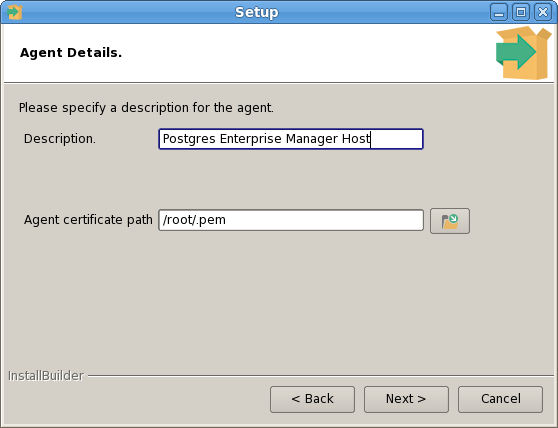
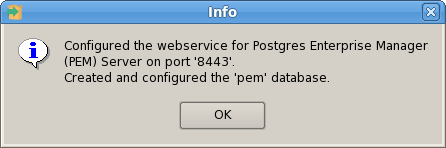
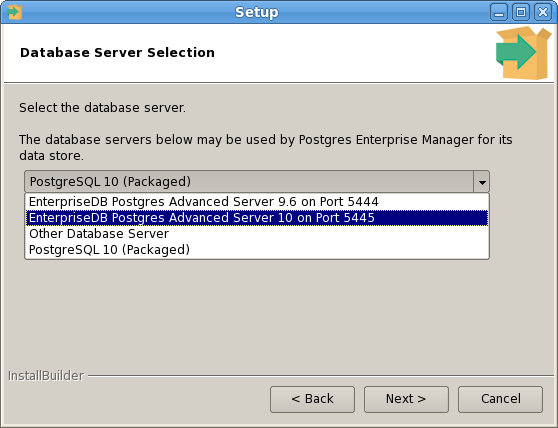
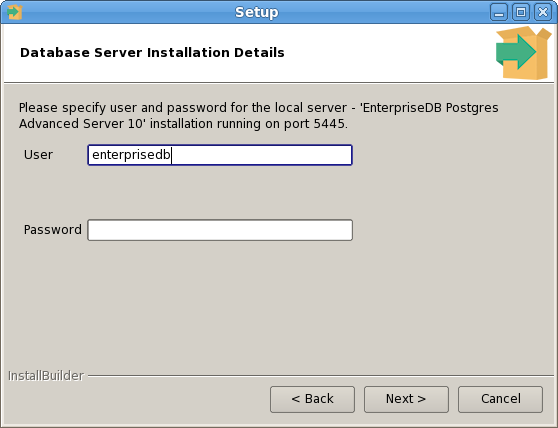
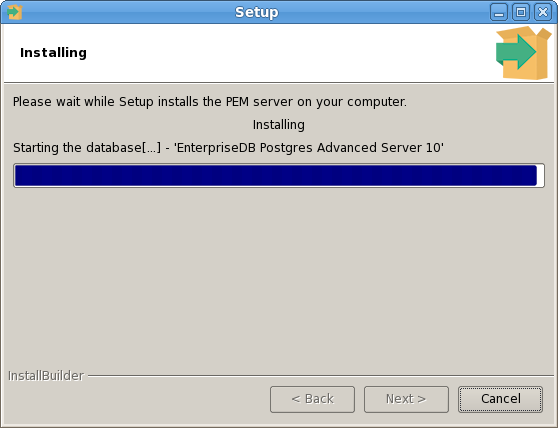
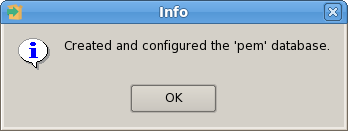
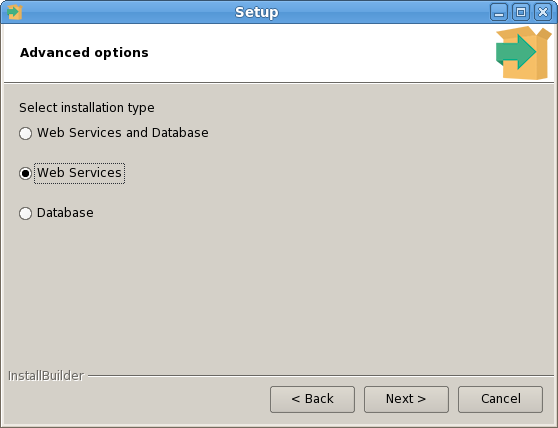
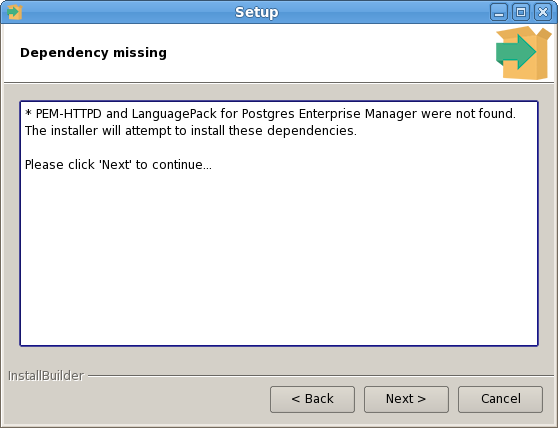
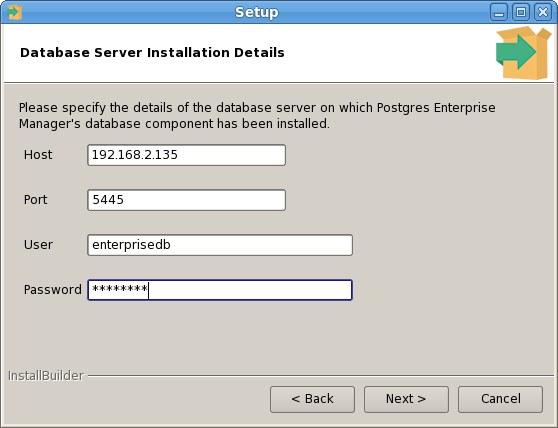
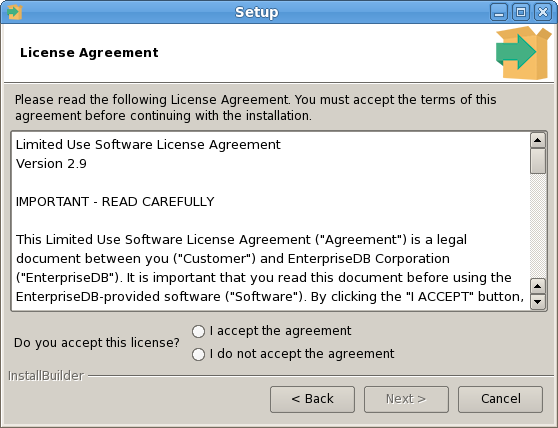
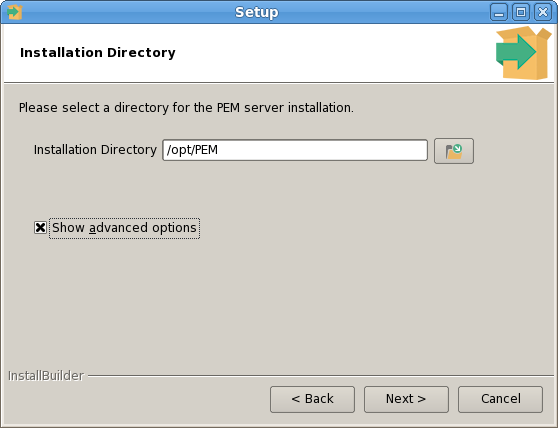
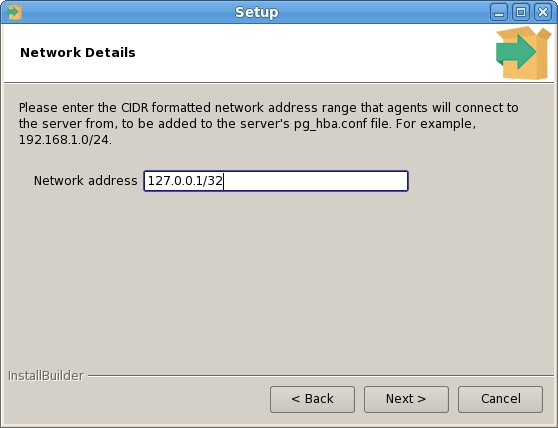
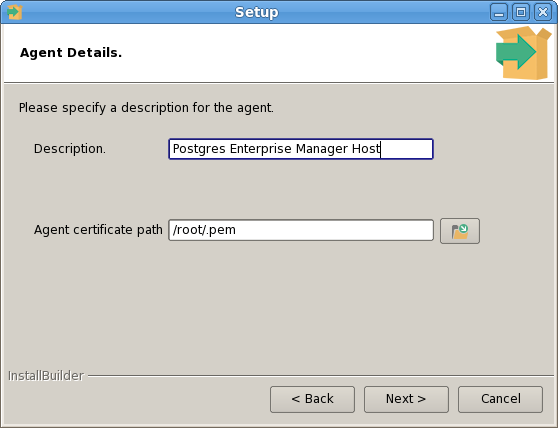
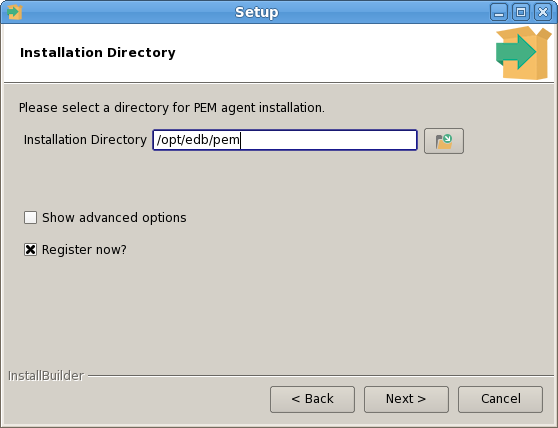
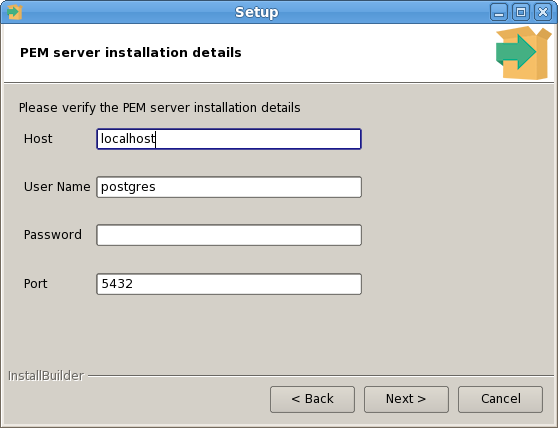
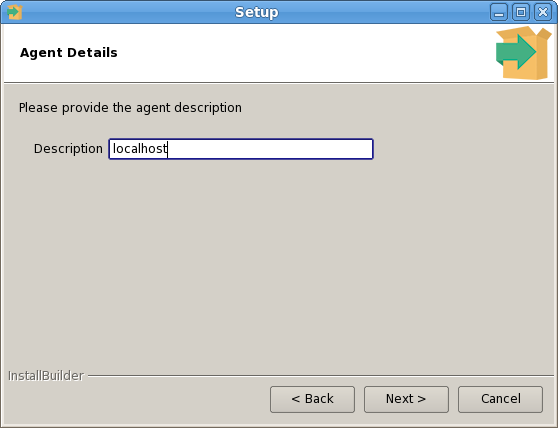
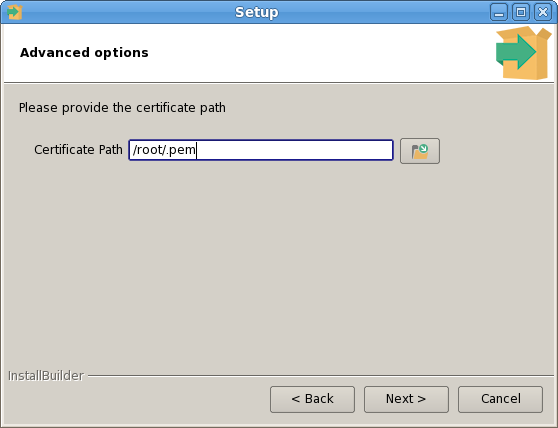
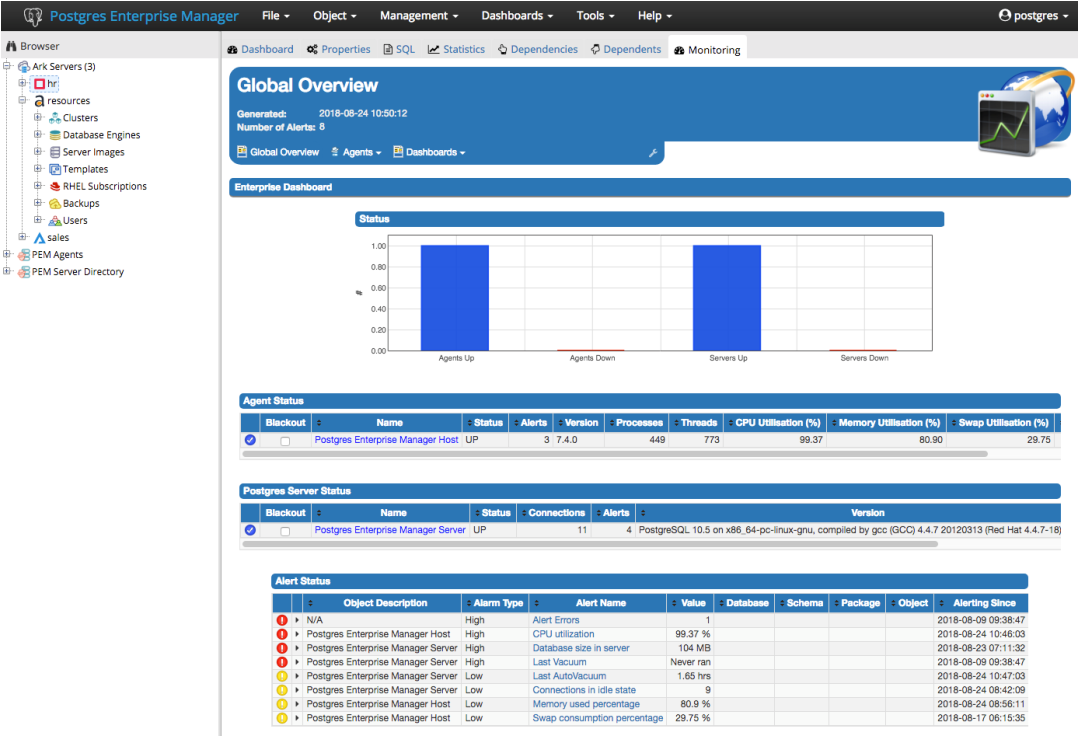
The PEM Agent installer creates two executables: the PEM worker (pemworker.exe) and the PEM agent (pemagent.exe). Each PEM worker has a corresponding PEM agent that you can use to start or stop the PEM worker. The PEM agent will also restart the PEM worker should it terminate unexpectedly.
The PEM worker log file contains information related to PEM worker activity (probe activities, heartbeat responses, etc.), and is stored in /var/log/pem/worker.log.